
How to Price Your SaaS Product: A Comprehensive Guide
If you’re in the business of selling software as a service (SaaS), then you know that pricing your product can be a tricky endeavor. After all, you want to make sure that you’re not leaving money on the table, but you also don’t want to price yourself out of the market. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll show you how to price your SaaS product so that you can maximize your revenue.

When it comes to pricing your SaaS product, there are a few different pricing models that you can choose from. The most common pricing models are subscription-based, usage-based, and feature-based. Let’s take a closer look at each of these pricing models so that you can decide which one is right for your business.
Subscription-based pricing is the most common pricing model for SaaS products. With this model, customers are charged a recurring fee on a monthly or yearly basis. The advantage of subscription-based pricing is that it provides predictable revenue for your business. The disadvantage is that it can be difficult to increase prices without losing customers.
Usage-based pricing is another popular option for SaaS products. With this model, customers are charged based on their usage of the product.
This type of pricing can be advantageous because it allows customers to only pay for what they use. However, it can be challenging to track usage and set prices that accurately reflect the value of the product.
Feature-based pricing is a third option that you may want to consider for your SaaS product. With this type of pricing, customers are charged based on the number or type of features that they use.
Feature-based pricing can be beneficial because it allows you to upsell customers on higher-priced plans with more features. However, it’s important to make sure that your prices accurately reflect the value of the features that you’re offering.
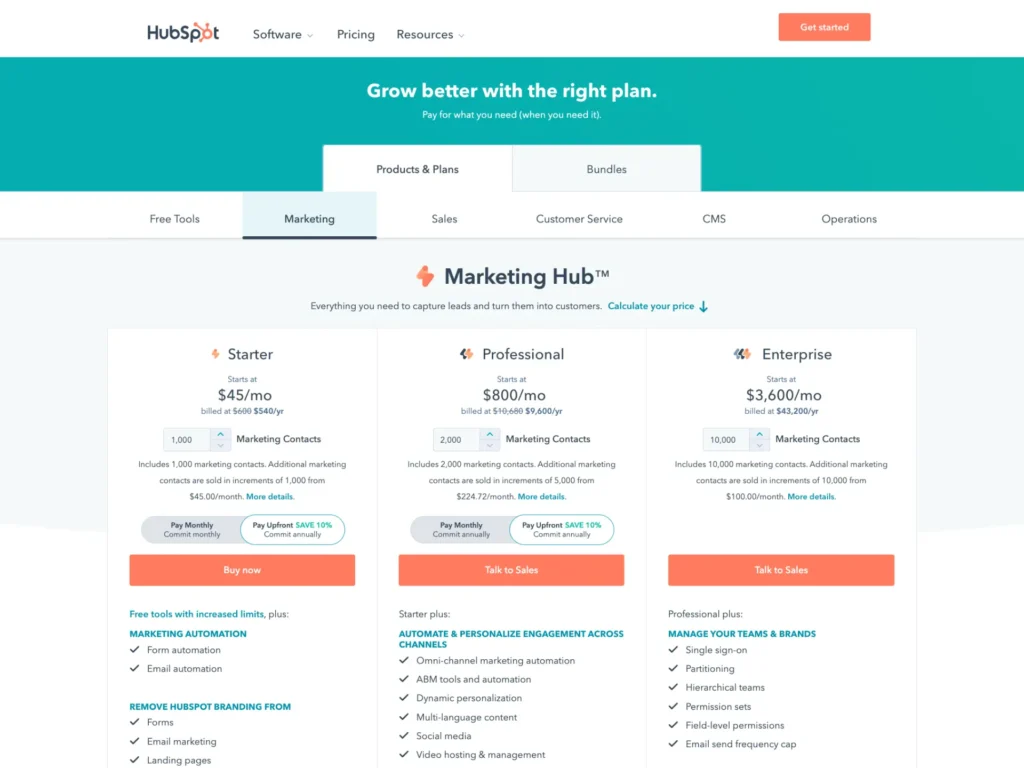
Once you’ve decided on a pricing model, you need to set a price point for your product.
When setting a price point, there are a few things that you need to consider.
First, you need to make sure that your price point is competitive with other products in the market.
Second, you need to make sure that your price point reflects the value that your product offers.
And third, you need to make sure that your price point is something that your target market is willing to pay.
Once you’ve considered all of these factors, it’s time to start testing different price points for your product.
One way to do this is through A/B testing. With A/B testing, you create two different versions of your product with different price points and see which one performs better with potential customers. This type of testing can be extremely helpful in finding the perfect price point for your product.
Another way to test different price points is through beta testing. With beta testing, you release your product at a certain price point and then gather feedback from users about how they feel about the price. This feedback can be extremely valuable in determining whether or not your current price point is working or if you need to adjust it up or down.
Once you’ve found a price point that works well for your product, it’s important to revisit your pricing on a regular basis and make adjustments as needed.
This will ensure that your prices always reflect the current value of your product and the current state of the market.
Pricing your SaaS product doesn’t have to be complicated or time-consuming. By following these simple tips, you can ensure that you’re always maximizing your revenue and keeping your customers happy.
Understanding Customer Needs to Determine SaaS Pricing
As a SaaS business, it’s critical that you understand your customer needs in order to determine the right pricing model. By understanding what your customers need, you can develop a pricing strategy that meets their needs and allows you to generate revenue.
There are a few key things to keep in mind when trying to understand customer needs:
Once you have a good understanding of the customer’s needs, you can start to develop a pricing strategy that meets their needs. Here are a few things to keep in mind when developing your pricing strategy:
- Offer a variety of pricing options.
- Be flexible with your pricing.
- Test your pricing models.
- Always be willing to negotiate.
By understanding your customer needs and offering a pricing model that meets their needs, you can ensure that your SaaS business is successful.
Developing a SaaS Pricing Structure
Developing a SaaS pricing structure can be a daunting task. There are so many factors to consider, from the cost of your product to the value it provides to your customers. It’s important to get it right, because the wrong pricing can cause your business to fail.
The good news is, there are some tried and true methods for coming up with a SaaS pricing model that will work for your business. In this blog post, we’ll explore some of the most popular pricing models and how to choose the right one for your business.
The most common pricing model for SaaS products is the subscription model. This model charges customers a recurring fee, typically on a monthly or yearly basis. The benefit of this model is that it provides a predictable revenue stream for your business.
The subscription model is generally the best option for businesses that have a continuous need for the product. For example, if you offer a service that helps businesses manage their finances, they are likely to need your service on an ongoing basis.
Another popular pricing model is the pay-as-you-go model. This model charges customers based on their usage of the product. This is a good option for businesses that don’t have a continuous need for the product, or for businesses that want to offer a free trial of the product.
The pay-as-you-go model is also a good choice if your product has different tiers of features, and you want to allow customers to pay for only the features they need. For example, if you offer a project management tool, you could have a basic plan that includes the core features, and then offer additional features in higher-priced plans.
The final pricing model we’ll discuss is the freemium model. This model offers a basic version of the product for free, and then charges customers for premium features. This is a good option if you want to attract a large number of users to your product.
The freemium model is also a good choice if you have a product that can be used in multiple ways. For example, if you offer a task management tool, you could allow users to create an unlimited number of tasks in the free version, but limit the number of users who can access the product, or charge for premium features like task collaboration or real-time updates.
No matter which pricing model you choose, it’s important to consider the value your product provides to customers. Make sure you’re not overcharging for your product, or customers will go elsewhere. And make sure you’re providing enough value to justify the price you’re charging.
The best way to do this is to start by offering a free trial of your product. This will allow potential customers to try out your product and see if it’s a good fit for their needs. Once they’ve had a chance to use your product, they’ll be in a better position to decide if they’re willing to pay for it.
If you’re not sure which pricing model to choose, or how to set your prices, start with a free trial and see how it goes. You can always adjust your prices later if you need to.
Choosing Your SaaS Pricing Tiers
When you’re running a software as a service (SaaS) business, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is how to price your product.
The wrong pricing can kill your business – if you charge too little, you may not be able to cover your costs or make a profit. If you charge too much, you may priced yourself out of the market.
When setting prices, you need to consider your costs, the value your product provides, and what the market will bear.
Your costs include both the direct costs of providing your product (such as hosting fees and employee salaries) and the indirect costs of marketing and selling your product.
The value your product provides is based on the benefits it delivers to customers. To determine the value of your product, ask yourself what problem it solves for customers and how much time or money it saves them.
The market will only bear so much – meaning that there is a limit to how much people are willing to pay for your product. To find out what the market will bear, you need to do market research to understand what similar products are selling for and what customers are willing to pay.
Once you have all of this information, you can start setting prices for your tiers. It’s important to remember that pricing is not a one-time decision – as your business grows and changes, your pricing should evolve as well.
The most important thing is to start with a pricing strategy that makes sense for your business and then adjust as needed over time. By taking the time to thoughtfully consider your options, you can ensure that you’re making the best decision for your business – now and in the future.
Basic & Advanced Features: Deciding What to Charge For
Most SaaS products have both basic and advanced features. The question then becomes, what do you charge for each?
The most common pricing model is to have a basic tier that is free or very cheap, and then charge for the advanced features. This has the advantage of getting users in the door, and then upselling them on the features they really need.
Another common pricing model is to have all features available at a single price point. This has the advantage of simplicity, but the downside is that some users will never use the advanced features and feel like they are overpaying.
So which model is right for your product? There is no easy answer, as it depends on your product, your target market, and your business goals.
If you’re not sure where to start, a good middle ground is to have a basic tier with limited features, and then a few different pricing tiers for the advanced features. This way, users can still get started for free or very cheap, but they have the option to upgrade to get access to the full range of features.
Whatever pricing model you choose, make sure to clearly communicate what is included in each pricing tier. Users should never feel like they are being nickel and dimed, or that they are missing out on essential features by not paying for the top tier.
If you’re not sure what to charge for your advanced features, start by looking at what other similar products are charging. You can also run some A/B tests to see how different pricing models impact your conversion rate. Ultimately, it’s up to you to decide what’s fair to charge for your product.
When it comes to SaaS products, there is no one-size-fits-all answer for pricing. The best way to figure out what to charge is to experiment and see what works best for your product and your business goals.
Handling Volume & Promotional Discounts
Volume discounts and promotional discounts can be a great way to increase sales and encourage customers to buy more of your products or services. However, if not managed properly, these discounts can also erode your profits and cause cash flow issues.
There are a few things to keep in mind when offering volume or promotional discounts:
1. Make sure you have enough margin to absorb the discount. It’s important to know your gross margin (revenue less cost of goods sold) and net margin (gross margin less all expenses) before offering any discounts. This will ensure that you’re still making a profit even after the discount is applied.
2. Be strategic about when and how you offer discounts. If you offer a volume discount, make sure it’s for a high enough quantity that the customer is really getting a deal. Otherwise, they might just purchase the lower quantity and you won’t see the benefit. Similarly, with promotional discounts, make sure the timing is right and that the promotion is for a product or service that you really want to move.
3. Communicate the discount clearly to your customers. Make sure they know exactly how much they need to purchase to get the discount, and when the discount expires. Otherwise, you might end up with a lot of returns or customers who are angry that they missed out on the deal.
4. Have a plan for when the discount ends. Once the discount period is over, make sure you raise your prices back to their regular levels. Otherwise, you’ll continue to lose money on every sale.
Offering volume and promotional discounts can be a great way to increase sales and encourage customers to buy more of your products or services. However, if not managed properly, these discounts can also erode your profits and cause cash flow issues. Use the tips above to make sure you’re able to offer discounts without jeopardizing your business.
Generating Revenue Through Indirect Pricing Models
As a business owner, you’re always looking for new ways to generate revenue and grow your business. When it comes to pricing models, there are a few different options you can choose from. But which one is right for your business?
The answer may lie in an indirect pricing model.
What Is an Indirect Pricing Model?
An indirect pricing model is a type of pricing model where the price of a product or service is not directly tied to the cost of production. Instead, the price is based on factors like market demand, perceived value, and competition.
This type of pricing model is often used for products or services that are difficult to price using a traditional cost-plus pricing model. For example, if you’re selling a unique product or service, it may be hard to determine the direct costs of production. In this case, an indirect pricing model may be a better option.
There are a few different types of indirect pricing models you can use for your business. Let’s take a look at a few of the most common.
Market-Based Pricing
Market-based pricing is a type of indirect pricing model where the price of a product or service is based on the current market conditions. This type of pricing is often used for products or services that are in high demand.
For example, if you’re selling a popular product, you may use market-based pricing to set your prices. In this case, you would look at what other businesses are charging for similar products and use that information to help you set your own prices.
Competition-Based Pricing
Competition-based pricing is another type of indirect pricing model. As the name suggests, this type of pricing is based on the prices of your competition.
With competition-based pricing, you would look at what your competitors are charging for their products or services and use that information to help you set your own prices. This type of pricing can be helpful if you’re selling a similar product or service as your competitors.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing is a type of indirect pricing model where the price of a product or service is based on the perceived value of the product or service. With this type of pricing, you would look at what your customers believe your product or service is worth and price it accordingly.
For example, if you’re selling a luxury product, you may use value-based pricing to set your prices. In this case, you would look at what your customers are willing to pay for the product or service and price it accordingly.
Benefits of Indirect Pricing Models
There are a few benefits of using an indirect pricing model for your business. Let’s take a look at a few of the most notable benefits.
Flexibility: One of the biggest benefits of using an indirect pricing model is that it’s flexible. With this type of pricing, you can change your prices as needed based on market conditions or customer demand. This can be helpful if you need to quickly adjust your prices to stay competitive or generate more revenue. Simplicity: Another benefit of using an indirect pricing model is that it’s simple. You don’t have to worry about the direct costs of production when setting your prices. This can be helpful if you’re selling a unique product or service that’s difficult to price using a traditional cost-plus pricing model.
Another benefit of using an indirect pricing model is that it’s simple. You don’t have to worry about the direct costs of production when setting your prices. This can be helpful if you’re selling a unique product or service that’s difficult to price using a traditional cost-plus pricing model.
Customer Focus: With an indirect pricing model, you can focus on your customers when setting your prices. This can be helpful if you want to ensure that your prices are fair and in line with what your customers are willing to pay.
Drawbacks of Indirect Pricing Models
There are a few drawbacks of using an indirect pricing model for your business. Let’s take a look at a few of the most notable drawbacks.
Less Predictable: One of the biggest drawbacks of using an indirect pricing model is that it’s less predictable. With this type of pricing, your prices can fluctuate based on market conditions or customer demand. This can make it difficult to budget and forecast your revenue.
Another drawback of using an indirect pricing model is that it requires more research. You need to spend time understanding the market conditions and customer demand before you can set your prices. This can be time-consuming and may not be feasible for all businesses. May Not Be Competitive: One final drawback of using an indirect pricing model is that it may not be competitive. If you’re not careful, you could end up charging too much or too little for your products or services. This could make it difficult to attract and retain customers.
Which Indirect Pricing Model Is Right for Your Business?
When it comes to choosing an indirect pricing model for your business, there are a few different options to choose from. The right option for your business will depend on a variety of factors, including your industry, business goals, and target market.
If you’re not sure which indirect pricing model is right for your business, consider talking to a pricing expert. They can help you understand the different options and choose the best option for your business.
Understanding the Impact of Metered SaaS Pricing
When it comes to metered SaaS pricing, there are two main types of models: subscription and usage. In the subscription model, customers pay a fixed monthly or annual fee, regardless of how much they use the software. In the usage model, customers are charged based on their actual usage of the software.
There are pros and cons to both pricing models. In the subscription model, customers know exactly how much they will be paying each month, which can help with budgeting. However, they may end up paying for features they don’t use if their usage is lower than average. In the usage model, customers only pay for what they use, so they can save money if their usage is low. However, their bills can fluctuate from month to month, which can be difficult to budget for.
So, which pricing model is right for you? It depends on your business and your customers. If you’re not sure which model would work best, it’s worth doing some testing to see what works best for your business.
Building Business & User Loyalty with Freemium Models
The freemium model has been effective in building both business and user loyalty by providing a free product or service with premium features that can be accessed by paying a subscription. This model has been used by companies such as Dropbox, Evernote, and Spotify, and has been successful in acquiring new users and retaining them as loyal customers.
There are several reasons why the freemium model is successful in building loyalty. First, it allows users to try out the product or service before commitment, which builds trust between the user and the company. Second, it allows users to gradually upgrade their subscription as their needs change, which keeps them engaged with the product. And third, it provides users with a sense of ownership over their data, which makes them more likely to continue using the product or service.
One of the key challenges for companies using the freemium model is to design their pricing structure in a way that encourages users to upgrade to a paid subscription. This can be done by offering a variety of pricing plans that offer different levels of features, or by offering discounts for users who commit to a longer-term subscription.
The freemium model is a great way to build business and user loyalty, and can be an effective way to acquire new users and retain them as customers. If you’re considering using the freemium model for your business, make sure to carefully consider your pricing structure to ensure that you’re encouraging users to upgrade to a paid subscription.
SaaS Pricing Challenges & Considerations
The pricing of a SaaS product can be a challenge for any business. There are many factors to consider when pricing a SaaS product, such as the features and function of the product, the target audience, the competition, and the overall market.
One of the most important factors to consider when pricing a SaaS product is the features and function of the product. The price of a SaaS product should be based on the value that it provides to users. For example, a SaaS product that provides a comprehensive CRM solution will be priced differently than a SaaS product that offers a simple task management tool.
Another important factor to consider when pricing a SaaS product is the target audience. The price of a SaaS product should be based on the needs of the target audience. For example, a SaaS product that is targeted at small businesses will be priced differently than a SaaS product that is targeted at enterprise businesses.
The competition is another important factor to consider when pricing a SaaS product. The price of a SaaS product should be competitive with other similar products on the market. For example, if there are two CRM products on the market that are similar in terms of features and price, the company that is offering the CRM product with the higher price will likely lose customers to the company that is offering the CRM product with the lower price.
The overall market is also an important factor to consider when pricing a SaaS product. The price of a SaaS product should be based on the current state of the market. For example, if the market for CRM solutions is currently saturated, the price of a new CRM solution will be lower than if the market for CRM solutions is currently undersaturated.
Pricing a SaaS product can be a challenge for any business, but it is important to consider all of the factors mentioned above when setting the price for a SaaS product.
Key Takeaways: Crafting a Winning SaaS Pricing Model
SaaS pricing models are complex and constantly evolving. In order to craft a winning model, you need to have a deep understanding of the various factors at play. In this blog post, we’ll share some key takeaways on crafting a winning SaaS pricing model.
1. The most important factor in any pricing model is value. You need to ensure that your pricing reflects the value that your product or service delivers.
2. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to pricing. The best pricing model for your business will depend on a variety of factors, including your target market, the nature of your product or service, and your competitive landscape.
3. Experimentation is key. Don’t be afraid to try out different pricing models and experiment with pricing strategies. The only way to find what works best for your business is to test and learn.
4. Be prepared to adjust your pricing model as your business evolves. As your business grows and changes, so too should your pricing model. What worked well in the early stages of your business might not be the right fit later on.
5. Always keep an eye on the competition. Be aware of how your competitors are pricing their products or services. This will give you a good benchmark to compare your own pricing against.
6. Make sure your pricing model is sustainable. A good pricing model should be sustainable in the long term. Avoid “cheap” pricing strategies that discount your product or service in the short term but are not sustainable over the long haul.
By following these key takeaways, you’ll be well on your way to crafting a winning SaaS pricing model for your business.


